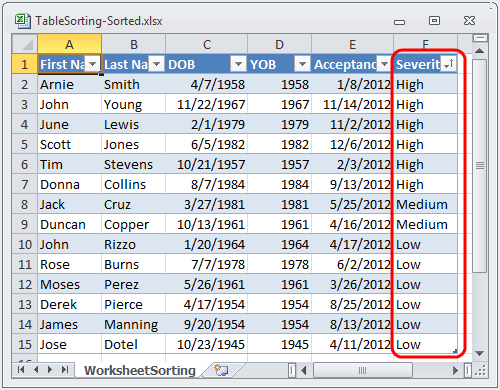
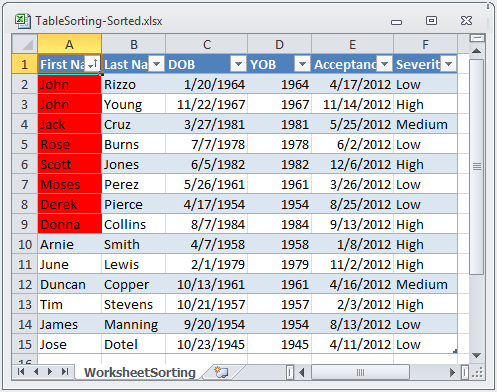
Sorting is done by setting a sorting condition on a table column. When a sorting condition is set on a column, all sort conditions in the table will be reevaluated to determine the order of the cells in the table. When cells need to be moved to meet their sort criteria, the entire row of cells in the table is moved as a unit. If the data in the table is subsequently changed, the sort condition will not be reevaluated.
The sort conditions in a table are only reapplied when sort conditions are added, removed, modified, or when the ReapplySortConditions method is called on the table.
When sorting conditions are reevaluated, only the visible cells are sorted. All cells in hidden rows are kept in place.
In addition to accessing sort conditions from the table columns, they are also exposed off the WorksheetTable.SortSettings SortConditions collection. This is an ordered collection of columns/sort condition pairs. The order of this collection is the precedence of the sorting. The first sort condition in the collection will be applied first, sorting all rows in the table by the values of the cells in the column sorted by that condition. If any groups of cells in that sorting have the same values, their rows are then sorted as a sub-group with the next sort condition, and so on.
The following sort condition types are available to set on columns:
| Sort condition type |
Description |
|
Sort cells in an ascending or descending order based on their value.
|
|
Sort cells in a defined order based on their text or display value. This might be useful for sorting as they appear on the calendar or as they appear in a custom list defined by you, rather than alphabetically.
|
|
Sort cells based on whether their fill is a specific pattern / gradient.
|
|
Sort cells based on whether their font is a specific color.
|
There is also a WorksheetTable.SortSettings CaseSensitive property which allows the developer to determine whether strings should be sorted case sensitively or not.