This topic is designed to help you understand the concept of responsive layout when the XamDataGrid control is rotated.
This topic contains the following sections:
Responsive layouts allow you to react to scenarios in your application where horizontal screen real estate is significantly reduced, such as when a device is rotated from a horizontal to a vertical orientation; in such cases retaining all XamDataGrid columns in a visible state may impair both readability of data as well as reducing the aesthetics of an application. Therefore, columns which display less critical information may be removed from view, while still displaying columns which contain the most relevant data.
This behavior essentially allows you to orchestrate which columns should assume or maintain a visible state via the use of two or more ResponsiveState objects, each associated with a specific numeric range based on minimum and maximum widths of the screen, thus allowing you to react dynamically to any changes to screen width densities within the XamDataGrid control.
The concept of responsive layout may be more easily understood by the following illustrations, which demonstrates a basic rotational layout scenario.
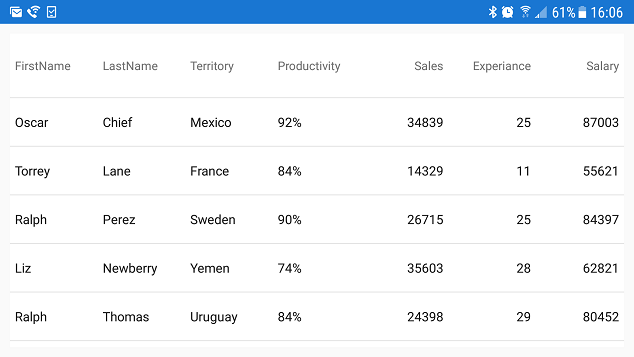
In the first screenshot, the XamDataGrid control is displayed in a horizontal orientation and it contains seven visible columns: First Name, Last Name, Territory, Productivity, Sales, Experience, and Salary.

In the second screenshot, the device has been rotated to the vertical orientation; as a result of the decrease in horizontal screen area, the width of the XamDataGrid control is also significantly reduced. All of the columns remain visible, having assumed a horizontally compressed appearance which not only makes discerning the presented data difficult by the user, but is also creating a generally unpleasant aesthetic and poor user experience:

However, with the responsive grid layout, this scenario may be reacted to by removing the least relevant columns (Experience, Territory, Salary) from view and redistributing the remaining columns to make use of this new space.

Before implementing responsive layout behavior, you need to prepare your application projects and save parameters of device’s screen because they will be later used to define ResponsiveState objects of the XamDataGrid control.
In the Portable application project, add this code to define parameters of device’s screen:
In C#:
public partial class App : Application
{
static public int ScreenWidth;
static public int ScreenHeight;
static public float ScreenDensity = 1;
...
}In the .Droid application project, add this code to save parameters of device’s screen:
In C#:
public class MainActivity : FormsAppCompatActivity
{
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle)
{
App.ScreenDensity = Resources.DisplayMetrics.Density;
App.ScreenWidth = Resources.DisplayMetrics.WidthPixels;
App.ScreenHeight = Resources.DisplayMetrics.HeightPixels;
...
}
}In the .iOS application project, add this code to save parameters of device’s screen:
In C#:
public partial class AppDelegate : FormsApplicationDelegate
{
public override bool FinishedLaunching(UIApplication app, NSDictionary options)
{
App.ScreenWidth = (int)UIScreen.MainScreen.Bounds.Width;
App.ScreenHeight = (int)UIScreen.MainScreen.Bounds.Height;
...
}
}Rotating a device which is running your application may drastically alter the available horizontal area of the XamDataGrid control in your application, this example will walk you through the process of implementing design pattern for responsive layout on device rotation, with the XamDataGrid control to compensate for this condition.
In your main view, implement 4 variables of type int to store dimension data for the device’s visible area, this data will be used to determine the device orientation.
In C#
static int ContentWidth = (int)(App.ScreenWidth / App.ScreenDensity);
static int ContentHeight = (int)(App.ScreenHeight / App.ScreenDensity);
static int ThresholdMax = Math.Max(ContentHeight, ContentWidth);
static int ThresholdMin = Math.Min(ContentHeight, ContentWidth);Create an instance of XamDataGrid control in your main view.
In C#:
var DataGrid = new XamDataGrid();
DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = true;
DataGrid.ItemsSource = SampleSalesPerson.GenerateSalesData(300);In XAML:
<ig:XamDataGrid x:Name="DataGrid" AutoGenerateColumns="True">
<ig:XamDataGrid.ItemsSource>
<local:SampleSalesTeam />
</ig:XamDataGrid.ItemsSource>
</ig:XamDataGrid>Add a helper method for creating ResponsivePhase objects as is demonstrated in code below:
In C#:
private ResponsivePhase CreatePhase(string columnName, string propertyName, object value)
{
var setter = new ColumnPropertySetter()
{
ColumnName = columnName,
PropertyName = propertyName,
Value = value,
};
return new ResponsivePhase().AddColumnPropertySetter(setter);
}Create an instance of the ResponsiveState class and define which columns should not be hidden in the landscape orientation as demonstrated in the following code snippet.
In C#:
var state1 = new ResponsiveState();
state1.Name = "Landscape State";
state1.MaximumWidth = ThresholdMax;
state1.MinimumWidth = ThresholdMin + 1;
state1.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Salary", "IsHidden", false));
state1.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Territory", "IsHidden", false));
state1.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Experience", "IsHidden", false));Next, create second instance of the ResponsiveState class and define which columns should be hidden in the portrait orientation as demonstrated in the following code snippet.
In C#:
var state2 = new ResponsiveState();
state2.Name = "Portrait State";
state2.MaximumWidth = ThresholdMin;
state2.MinimumWidth = 0;
state2.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Salary", "IsHidden", true));
state2.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Territory", "IsHidden", true));
state2.AddResponsivePhase(CreatePhase("Experience", "IsHidden", true));Add both ResponsiveState objects to the XamDataGrid control as shown in this code snippet:
In C#:
DataGrid.ResponsiveStates.Add(state1);
DataGrid.ResponsiveStates.Add(state2);Save and run your application to verify the responsive layout behavior of the XamDataGrid control.
Orienting the device horizontally, (causing it to assume a landscape mode) the XamDataGrid control will display all 7 columns: First Name, Last Name, Territory, Productivity, Sales, Experience, and Salary.

Changing the device orientation from a horizontal to a vertical orientation will cause the device to assume portrait mode and the XamDataGrid control will hide Experience, Territory, and Salary columns from view and display only 4 columns as illustrated in the following image:

The following table lists topics that are related to this topic: